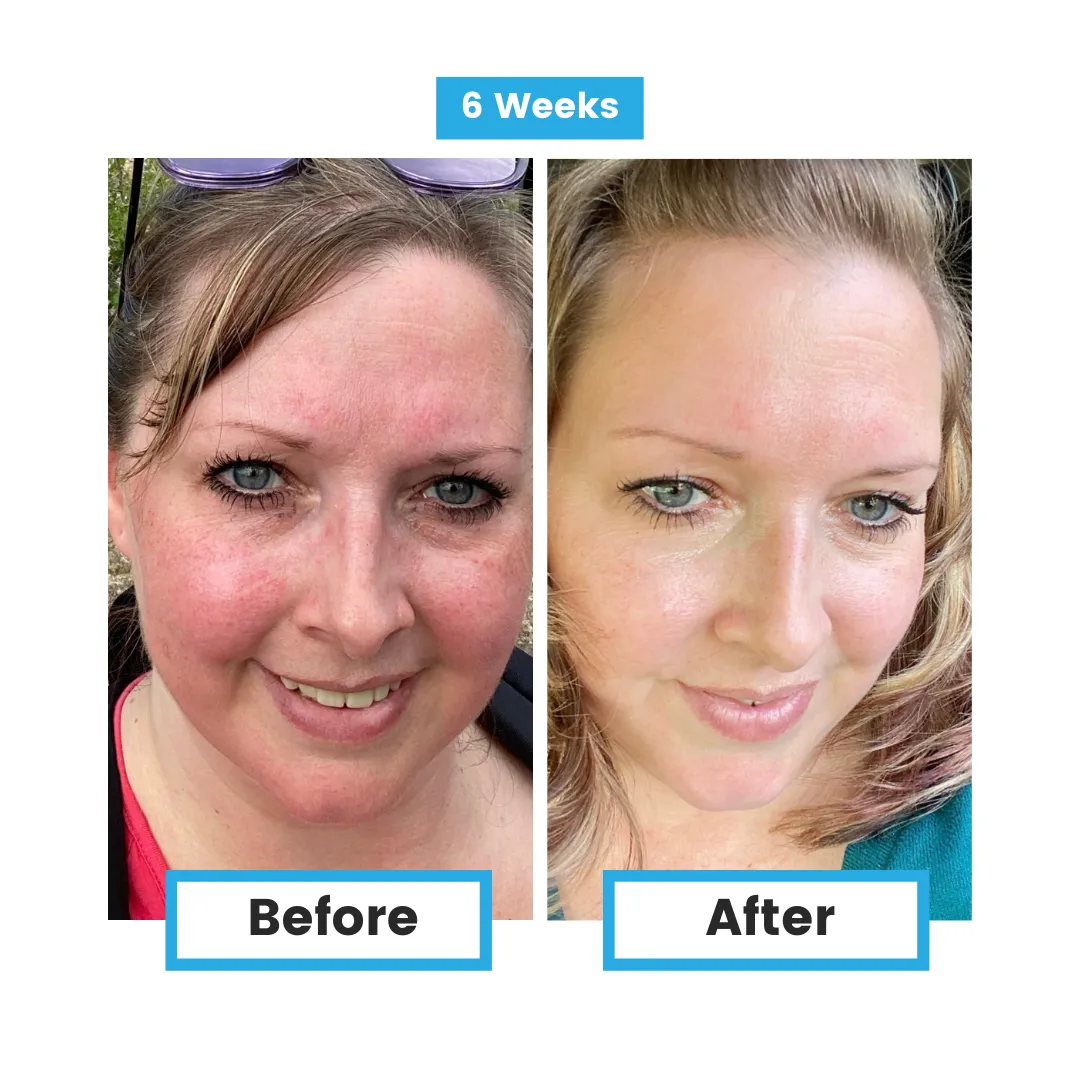
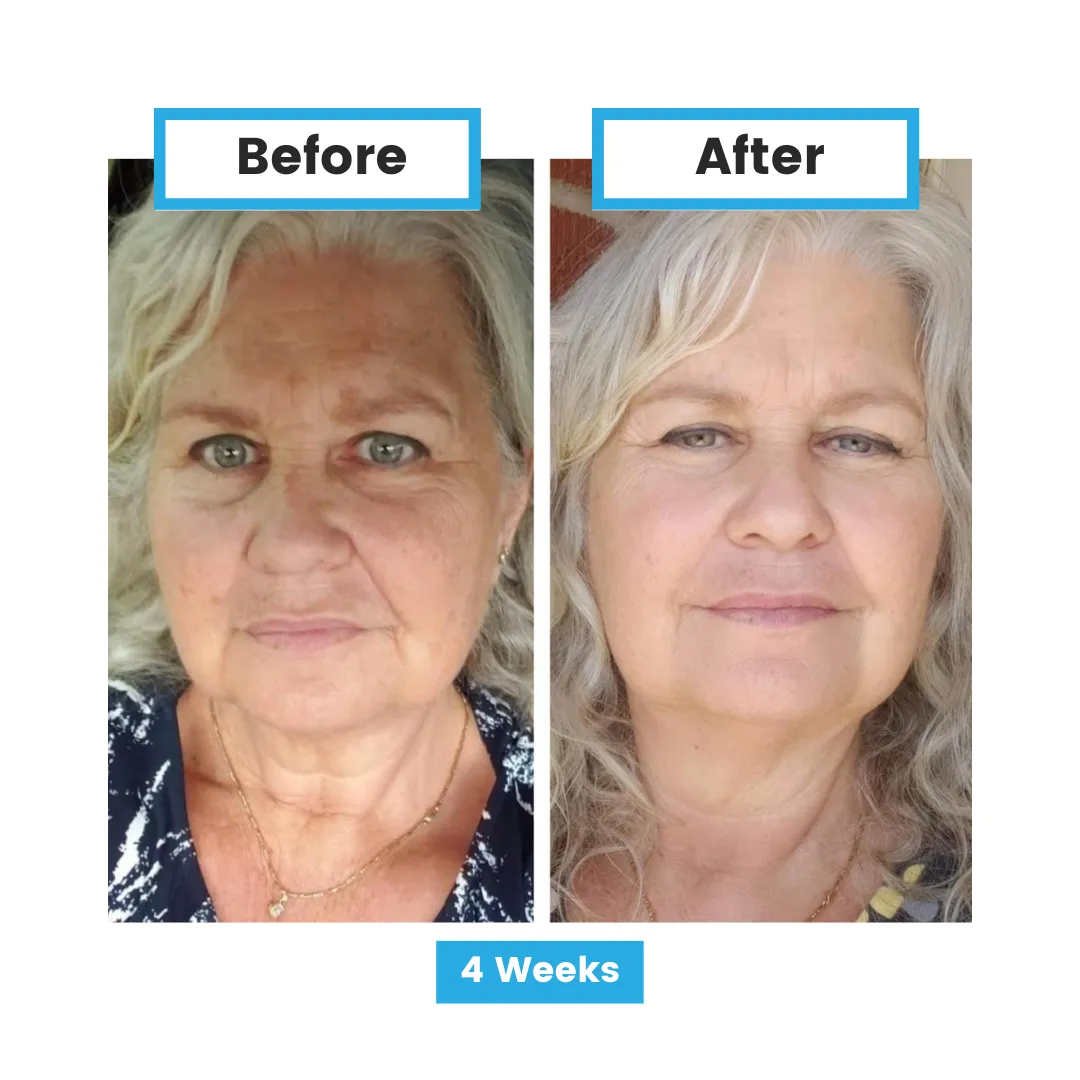
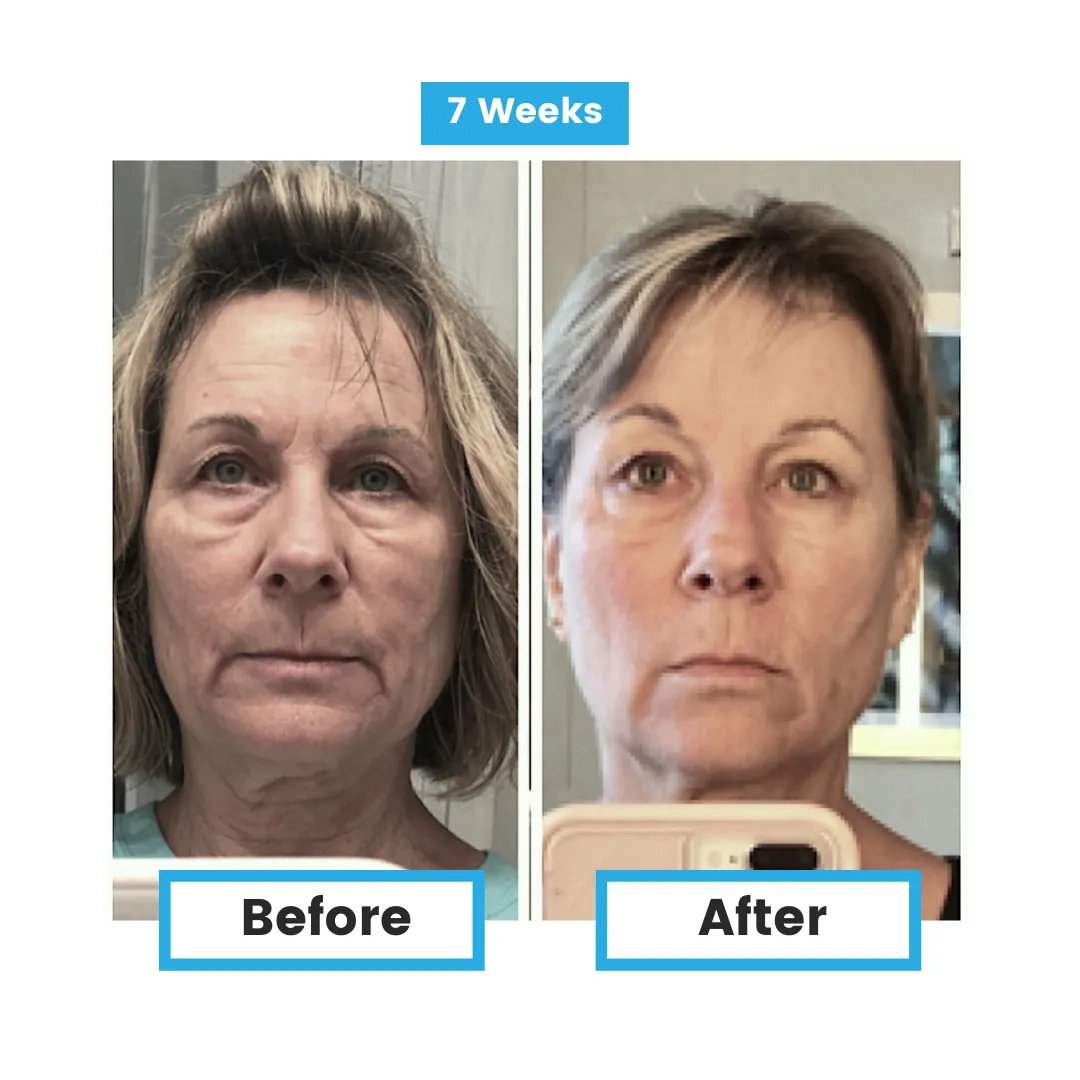
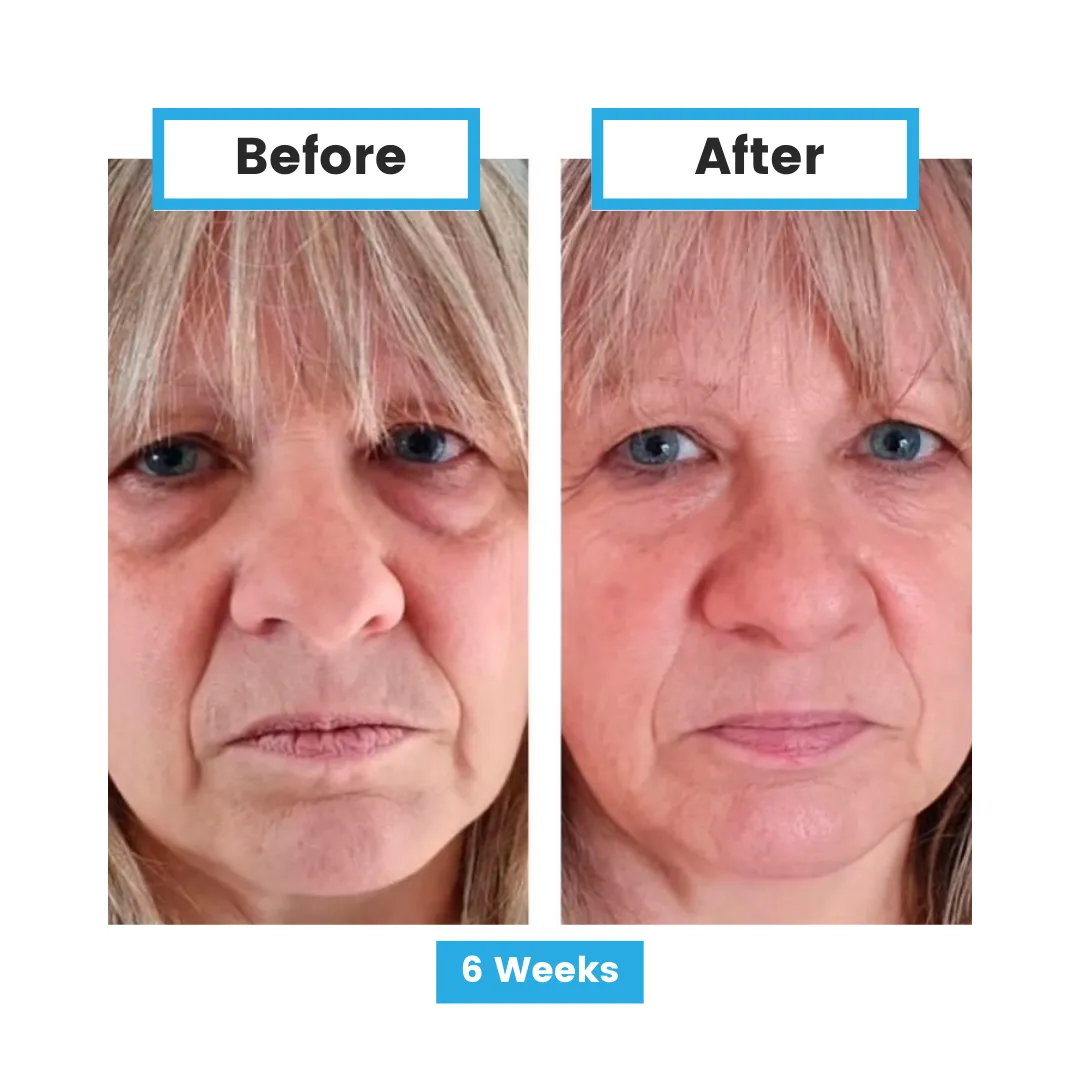
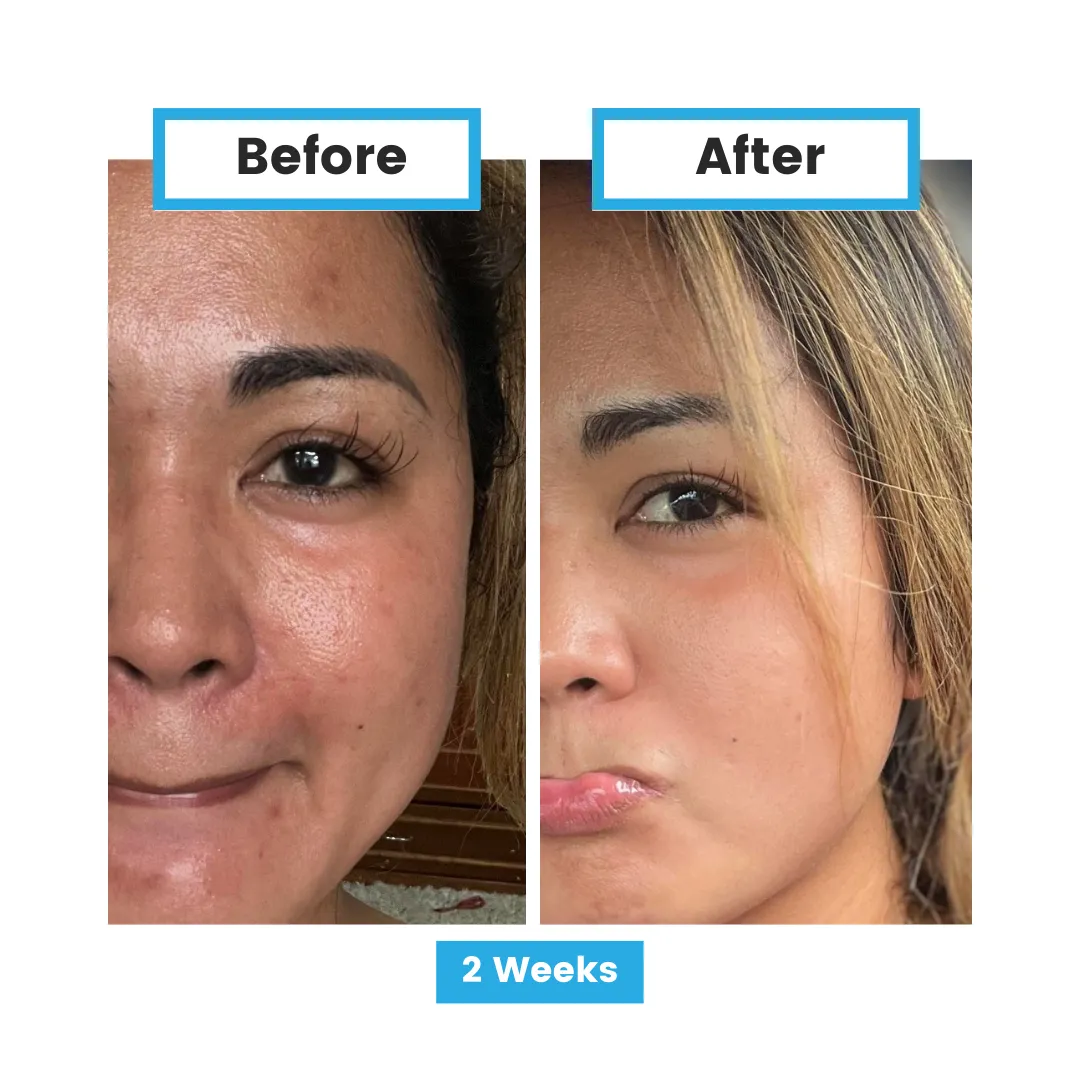
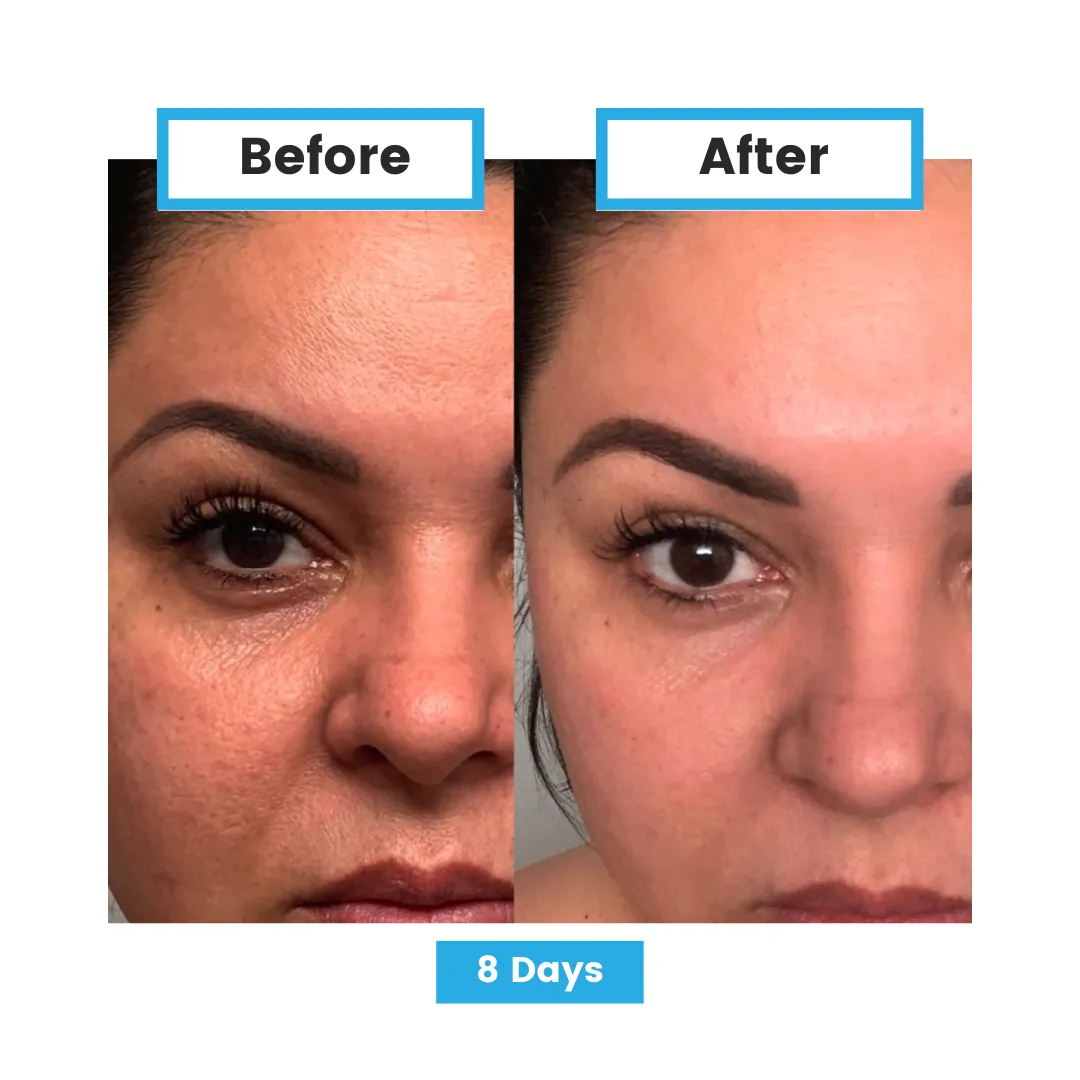
Glutathione and Disease
189,000+ Published Studies/Articles
What is Glutathione?
Start Here:
Glutathione: overview of its protective roles, measurement, and biosynthesis
Diabetes
How oxidative stress contributes to the onset and progression of type 2 diabetes (T2D) and evaluates the potential benefits of glutathione (GSH) and its precursors, N-acetyl-cysteine (NAC) and glycine (GLY), in mitigating this stress.
Heart Disease
How glutathione, a vital antioxidant, helps protect the heart and blood vessels from damage caused by oxidative stress. The research highlights that maintaining adequate glutathione levels is crucial for cardiovascular health, as its deficiency can lead to increased oxidative stress, contributing to the development of heart diseases.
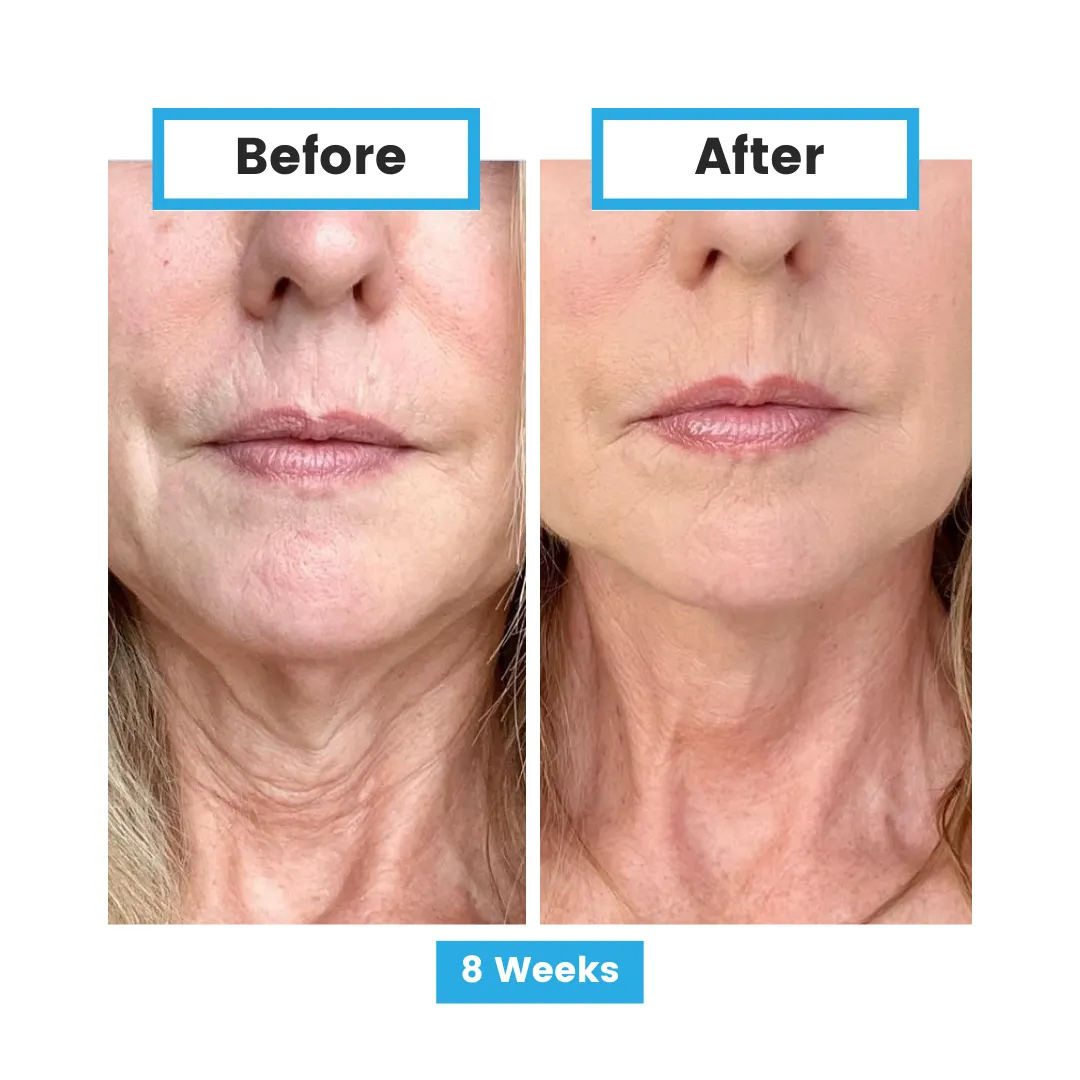
Skin Health
Oxidative stress, resulting from an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants, plays a significant role in skin health. It contributes to various skin conditions, including aging, inflammatory disorders, and cancer.
Stress and Mental Health
Low levels of glutathione, a key antioxidant in the brain, may make individuals more susceptible to mental health issues like depression, schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and anxiety. This finding highlights the importance of maintaining adequate glutathione levels for mental well-being.
Immune Function
Glutathione plays a crucial role in maintaining a balanced immune system. It supports the proper function of T-cell lymphocytes, which are essential white blood cells that defend the body against infections. Additionally, glutathione helps regulate cytokines—proteins that facilitate communication between immune cells—ensuring an appropriate immune response.
Liver Detoxification
Glutathione plays a crucial role in mitigating liver damage caused by alcoholism and hyperglycemia, highlighting its importance in maintaining liver health under these conditions.
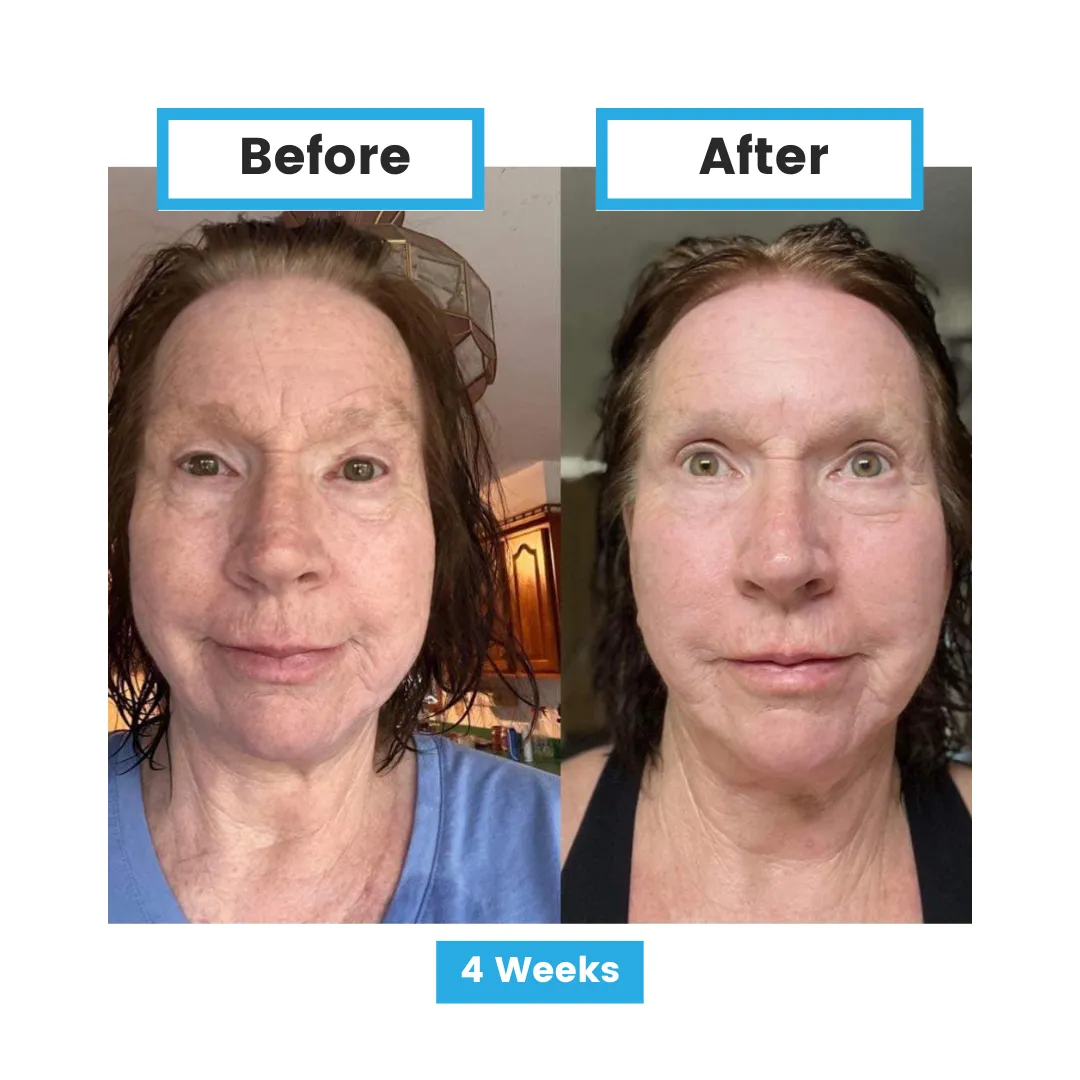
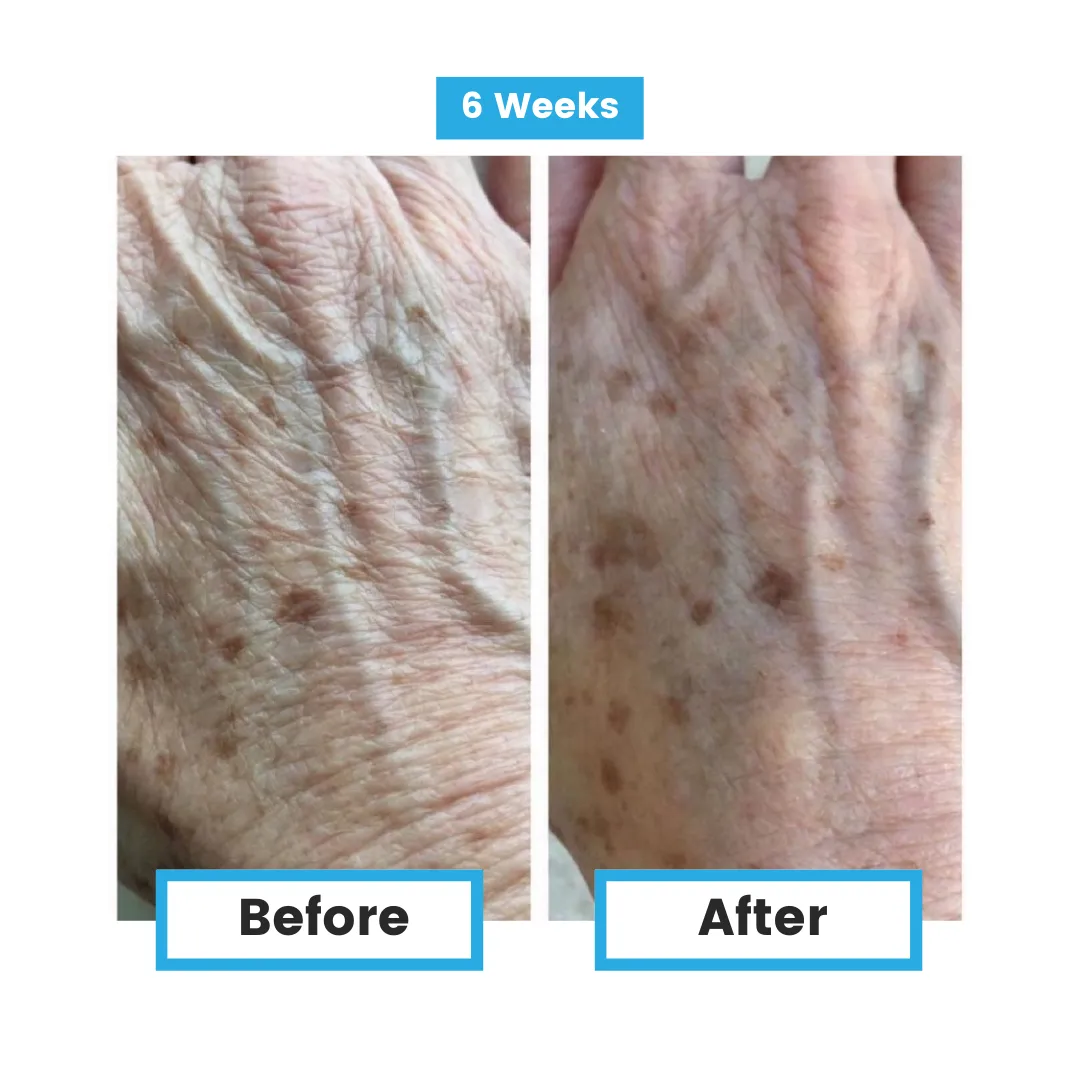
Aging and Age-related Diseases
Lower levels of glutathione are linked to a faster development of multiple chronic diseases in older adults. Higher glutathione levels were associated with better health and slower disease progression, highlighting its role in protecting against aging-related conditions. This suggests that maintaining healthy glutathione levels could be key to aging well.
https://academic.oup.com/biomedgerontology/article/75/6/1089/5479550
Brain Health
Impairment of glutathione function in the brain is linked to loss of neurons during the aging process or as the result of neurological diseases such as Huntington’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, stroke, and Alzheimer’s disease.
Cancer
Low levels of glutathione, a key antioxidant, are linked to the development and progression of cancer. This deficiency can lead to increased oxidative stress and DNA damage, which are common in many tumors.
Covid-19
Hospitalized COVID-19 patients exhibit severe glutathione deficiency and increased oxidative stress, which worsen with age, indicating that low glutathione levels may contribute to the severity of COVID-19.
Gut Health
Gut bacteria significantly influence the body's glutathione metabolism by consuming glycine, a crucial amino acid for glutathione synthesis, leading to reduced glutathione levels in the liver and colon. This interaction suggests that an imbalance in gut microbiota can deplete glutathione, potentially increasing oxidative stress and contributing to various diseases.
https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2015/11/151106062708.htm?utm_source=chatgpt.com
Chronic Fatigue
Individuals with CFS had reduced glutathione concentrations in the anterior cingulate cortex, a brain region associated with functions like emotion regulation and cognitive processing. This reduction suggests that oxidative stress and impaired energy metabolism may play roles in the development of CFS.
Lung Health
Individuals with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) exhibit significantly reduced glutathione levels in their lungs. This deficiency contributes to increased oxidative stress and inflammation, which are key factors in the progression of COPD. Supplementing glutathione has been proposed as a strategy to counteract oxidative damage and support respiratory health.
https://respiratory-research.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1465-9921-8-48
Toxin Exposure and Recovery
Glutathione plays a critical role in detoxifying harmful environmental toxins like pesticides and heavy metals. Glutathione protects cells from oxidative stress by neutralizing these toxins and facilitating their removal from the body. Maintaining healthy glutathione levels is essential for supporting the body’s natural detoxification processes and reducing toxic load.
A deficiency in glutathione synthetase impairs glutathione production, leading to symptoms like anemia, metabolic acidosis, frequent infections, seizures, intellectual disability, and loss of coordination
https://rarediseases.info.nih.gov/diseases/10047/glutathione-synthetase-deficiency
Copyright © 2026. Let's Build Health is a collaboration of distributors for HydrastatTM. All Rights Reserved